In a startling revelation, a Colorado-incorporated firm has been connected to Xinbi Guarantee, a Chinese illicit marketplace that has reportedly served as a hub for scammers throughout Southeast Asia, accumulating a staggering $8.4 billion in cryptocurrency transactions primarily in Tether (USDT). This report, released by blockchain security firm Elliptic, highlights how Xinbi operates as a black-market platform, providing services that range from money laundering to selling stolen personal data and fraudulent documents.
Xinbi Guarantee, described by its operators as an “investment and capital guarantee group company,” operates through Xinbi Co. Ltd, which was officially registered in Colorado in 2022. However, the company’s status has recently changed to “Delinquent” after failing to file a mandatory periodic report as of January 2025. The marketplace is particularly alarming as it functions mainly on Telegram, the popular messaging app, and has become a crucial tool for scammers engaged in “pig butchering” scams—frauds that manipulate victims into investing in fictitious schemes.
“The $8.4 billion in transactions should be considered a lower bound,” noted Elliptic researchers, emphasizing the potential underreporting of illicit activities occurring on the platform.
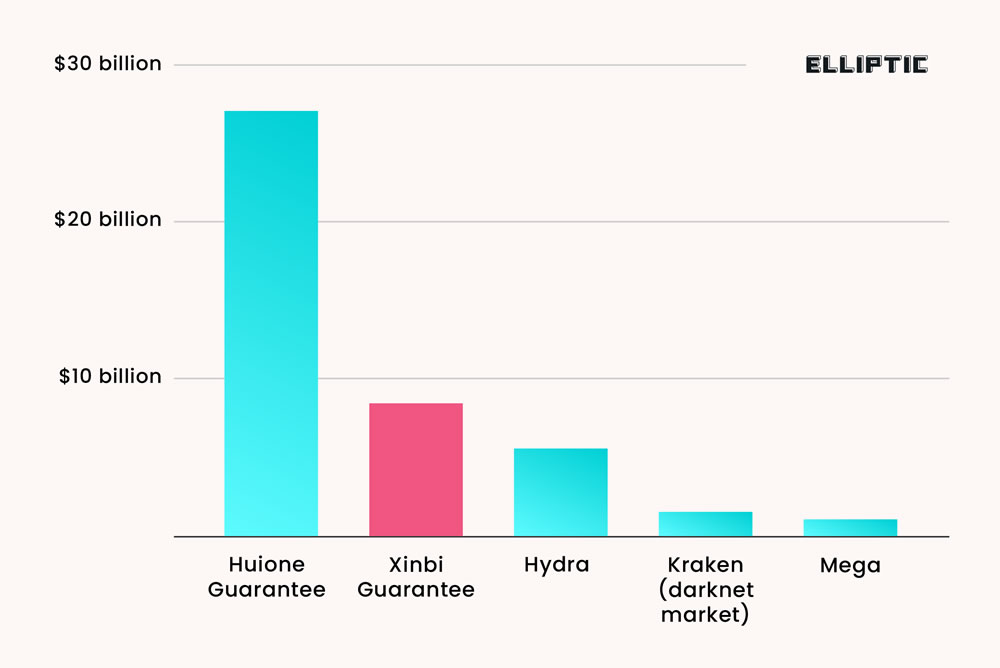
With a user base of approximately 233,000, Xinbi Guarantee is identified as the second-largest online black market, following closely behind Huione Guarantee, another notorious platform exposed by Elliptic in July 2024. This earlier platform was labeled as a major money-laundering operation by the US Treasury, having facilitated over $98 billion in transactions. The troubling trend of increasing transaction volumes across these platforms points to a broader underground banking system within China that heavily relies on stablecoins and digital payments for large-scale money laundering operations.
This fresh investigation underscores significant concerns surrounding the intersection of cryptocurrency and crime, raising critical questions about regulatory oversight and the efficacy of measures to combat such illicit activities in the digital space.
Illicit Marketplace Linked to Crypto Scams
This topic outlines the alarming connections between a Colorado-based firm and an illicit Chinese online marketplace, essentially unveiling a significant threat to individuals who may be targeted by scammers.
- Connection to Xinbi Guarantee:
- Linked to a Chinese illicit marketplace serving Southeast Asian scammers.
- Facilitates billions of dollars in cryptocurrency transactions, primarily in Tether (USDT).
- Services Offered to Scammers:
- Money laundering services as the largest category.
- Technology provision for scams, including Starlink equipment.
- Access to stolen personal data, fake IDs, and fraudulent documents.
- Marketplace Growth:
- Over $8.4 billion transacted to date, with rapid growth in transaction volume.
- 233,000 users actively participating in the marketplace.
- Legitimization and Legal Concerns:
- Xinbi Co. Ltd incorporated in Colorado in 2022; marked ‘Delinquent’ in 2025 for failing to file reports.
- Potential legal ramifications for businesses associated with illicit activities.
- Implications for Readers:
- Heightened awareness of potential scams, especially “pig butchering” scams targeting victims.
- Understanding the risks associated with cryptocurrency transactions and investment.
- Encouragement to protect personal information and be cautious of investment opportunities that seem too good to be true.
Elliptic underscores the necessity for vigilance and robustness in cybersecurity measures in light of a growing global illicit marketplace.
Examining the Rise of Xinbi Guarantee: A Look into Illicit Marketplaces
The recent revelations regarding Xinbi Guarantee, a Colorado-based company linked to a sprawling Chinese illicit marketplace, underscore the burgeoning challenges faced by law enforcement and cryptocurrency regulators. While Xinbi has made headlines for its astounding transaction volume of $8.4 billion and its operation of a fraud-ridden ecosystem, it is not alone in the underground economy. The comparative analysis with Huione Guarantee, another notorious marketplace operating on similar foundations, provides insight into both the competitive edges and pitfalls that these platforms present.
Competitive Advantages
Both Xinbi Guarantee and Huione Guarantee thrive on an innovative “guarantee model” that enhances user trust among vendors by requiring deposits. This feature minimizes fraud risks and facilitates large transaction volumes, making these platforms highly appealing to scam operators. The Telegram-based interface further increases accessibility, allowing scam merchants in Southeast Asia to easily communicate and operate effectively. With an active user base of 233,000, Xinbi offers a network size that rivals that of Huione, demonstrating its robust outreach in the shadowy corners of the cryptocurrency world.
Disadvantages and Regulatory Challenges
Despite the apparent advantages, these platforms face significant obstacles. Xinbi, for instance, has been labeled “delinquent” for failing to maintain required corporate filings, exposing vulnerabilities that could lead to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Furthermore, its identification as an illicit enterprise could prompt collaboration among international law enforcement agencies, putting its operators at greater risk. Huione Guarantee’s recent designation by the US Treasury as a money-laundering operation serves as a critical reminder that such platforms can quickly become targets for regulatory crackdowns, which could hinder operations significantly.
Beneficiaries and Possible Affected Parties
The ramifications of these illicit marketplaces extend beyond mere transaction bans; they affect various stakeholders. Scammers utilizing these platforms benefit immensely by accessing sophisticated methods for laundering money and acquiring illicit technology. Conversely, legitimate cryptocurrency firms and investors may experience increased scrutiny and doubt in the wake of widespread associations with scams and illegal activities, potentially undermining trust in the crypto ecosystem as a whole. The overarching presence of these platforms complicates the landscape for ethical users who prioritize compliance and transparency, creating substantial risk in the broader financial environment.