The cryptocurrency market is experiencing notable fluctuations, particularly with Ether (ETH), which saw a significant price drop of 9.3% from March 26 to March 28. This decline marks the first time in two weeks that ETH has tested the critical ,860 price level, raising alarms among traders and investors alike. The effect of this downturn was pronounced, leading to over 4 million in liquidations of leveraged ETH futures. As a result, the premium that ETH futures typically carry over the regular spot market has plummeted to its lowest level in over a year.
Traders are pondering whether the current low premium on ETH futures is a sign of a market bottom. Typically, ETH’s monthly futures trade at a premium to the spot price due to factors like longer settlement periods and sellers’ demand for compensation. However, recent data suggests that the futures premium has dropped significantly, reflecting a lack of interest in leveraged buying, which could indicate bearish sentiment.
“The current 2% ETH futures annualized premium suggests a lack of demand for leveraged longs (buys),” stated an analyst from Laevitas.ch.
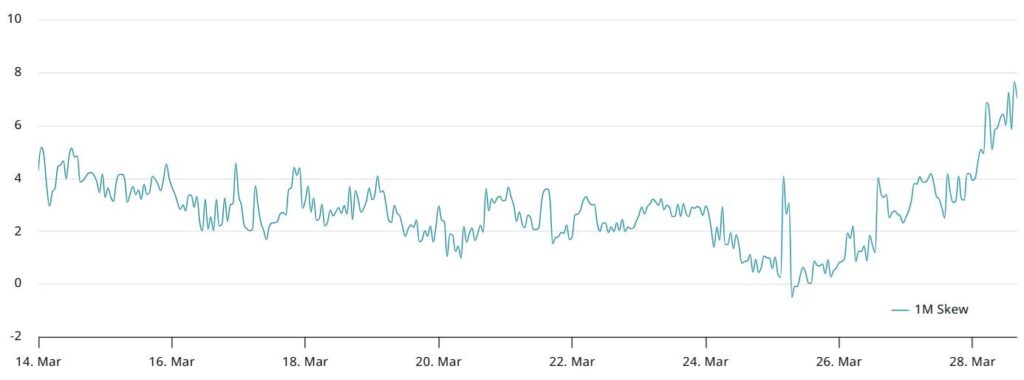
Moreover, market indicators show that ETH whales—large holders of Ether—are wary of further price drops. The 25% delta skew metric for ETH options indicates a rise to 7%, suggesting that professional traders are anticipating a downtrend, enhancing the risk of continued bearish momentum.
Several contributing factors could be impacting Ether’s market position. Analysts point to a decline in network activity and the increasing competitiveness of Ethereum’s blockchain landscape, with rivals like BNB Chain and Solana gaining ground. Furthermore, innovative projects such as Ethena plan to transition to their own layer-1 blockchains, which could divert users and capital away from Ethereum.
Despite the current challenges, some experts caution against quick conclusions. Ethereum is preparing for a significant protocol update known as the Pectra upgrade, which aims to enhance usability and address concerns around transaction fees. How this upgrade will impact Ether’s performance in the broader altcoin market remains to be seen, but it could be a game-changer for both investors and the framework of Ethereum itself.
Ethereum (ETH) Price Analysis and Market Trends
The recent drop in Ethereum’s price and its implications for traders and investors are significant. Here are the key points from the article:
- Price Correction:
- ETH price fell by 9.3% from March 26 to March 28, testing the ,860 level.
- This correction resulted in over 4 million in liquidations of leveraged ETH futures.
- Futures Market Insights:
- The futures premium dropped to its lowest level in over a year, indicating a shift in market sentiment.
- A 2% annualized premium suggests a lack of demand for leveraged long positions.
- Whale Behavior:
- The 25% delta skew for ETH options stands at 7%, indicating increased demand for put options as traders anticipate further price declines.
- Current data suggests professionals lack confidence in ETH’s near-term price recovery.
- Network and Market Competition:
- Declining Ethereum network activity is impacting demand as competitors like BNB Chain and Solana increase their presence.
- Innovative projects, such as Ethena, are migrating away from Ethereum, which could further diminish its ecosystem.
- Upcoming Protocol Upgrade:
- Investors are encouraged to monitor the upcoming Pectra upgrade, which may enhance Ethereum’s base layer fees and usability.
- The success of this upgrade could influence ETH’s performance in the broader altcoin market.
This information is vital for investors considering their positions in the Ethereum market, especially regarding risk management and future trading strategies.
Ethereum’s Recent Price Struggle: An In-Depth Competitive Analysis
The recent decline in Ethereum’s price has sent ripples through the cryptocurrency market, raising questions about its future performance and competitive standing. As Ether (ETH) faced a 9.3% drop from March 26 to March 28, reaching a critical support level of ,860, significant liquidation of leveraged futures followed. This situation starkly contrasts with Ethereum’s historical resilience, leading to growing concerns among traders regarding its market dynamics.
Competitive Advantages: Despite the current turmoil, Ethereum still benefits from its robust ecosystem, a large and engaged community, and continuous technological upgrades. Notably, the upcoming Pectra upgrade could enhance usability and potentially stabilize base layer fees, positioning Ethereum as a long-term player in the blockchain space. Furthermore, Ethereum maintains substantial liquidity compared to smaller competitors, providing a safety net for investors and traders.
Competitive Disadvantages: On the flip side, Ethereum faces increasing competition from emerging blockchains like BNB Chain and Solana, which offer specific functionalities catering to evolving market demands. The rise of layer-2 solutions is particularly concerning, as they siphon off transactional activity from Ethereum, impacting its network’s growth and profitability. Moreover, declining on-chain activity, coupled with a notable drop in the futures premium, indicates a wavering confidence among traders and suggests that ETH’s market dominance is being challenged.
This precarious situation could prove problematic for investors who are heavily leveraged in ETH futures, as evidenced by the substantial liquidations. Conversely, it might create opportunities for savvy traders willing to capitalize on the low premium and potential rebound post-upgrade.
Target Audience: The recent developments in Ethereum are crucial for different segments of the market. Retail investors and traders focusing on short-term price movements may find themselves at risk if the bearish trend continues. Conversely, long-term holders and those interested in Ethereum’s technological advancements could benefit from observing the potential impacts of the Pectra upgrade. Moreover, institutional investors may need to consider adjusting their strategies to mitigate risks associated with increased competition and shifting market dynamics.