The cryptocurrency landscape is buzzing with analysis surrounding Ethereum’s ongoing evolution, specifically its venture into layer-2 (L2) blockchain scalability. A recent report from Binance Research highlights a potential risk: while these L2 networks aim to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, they may also inadvertently undermine the value of Ether (ETH), the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
“Ethereum’s dominance in decentralized exchange volume and fee generation is currently under threat from competitors like Solana and BNB Smart Chain,” the report elaborates, signaling shifting tides in the blockchain domain.
Ethereum has long been a key player in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, but issues such as slow transaction speeds and high costs have led to concerns about its competitiveness. As L2 solutions emerge and gain popularity, the fragmentation of developer attention and liquidity could negatively impact Ethereum’s base layer, central to Ether’s value proposition.
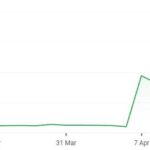
In light of Ether’s recent price drop—which saw it fall to $1,410 on April 7, the lowest point since March 2023—analysts are increasingly questioning the mainnet’s economic incentives. The fall represents a staggering decline of over 61% from its late 2024 peak above $4,100, as noted by Cointelegraph Markets Pro data.
“The upcoming Pectra upgrade, scheduled for May 7, aims to address staking and scalability concerns,” emphasizes the Binance report, but many believe that meaningful improvements to value accrual may still be on the horizon, especially with significant upgrades like Fusaka expected to roll out in 2025.
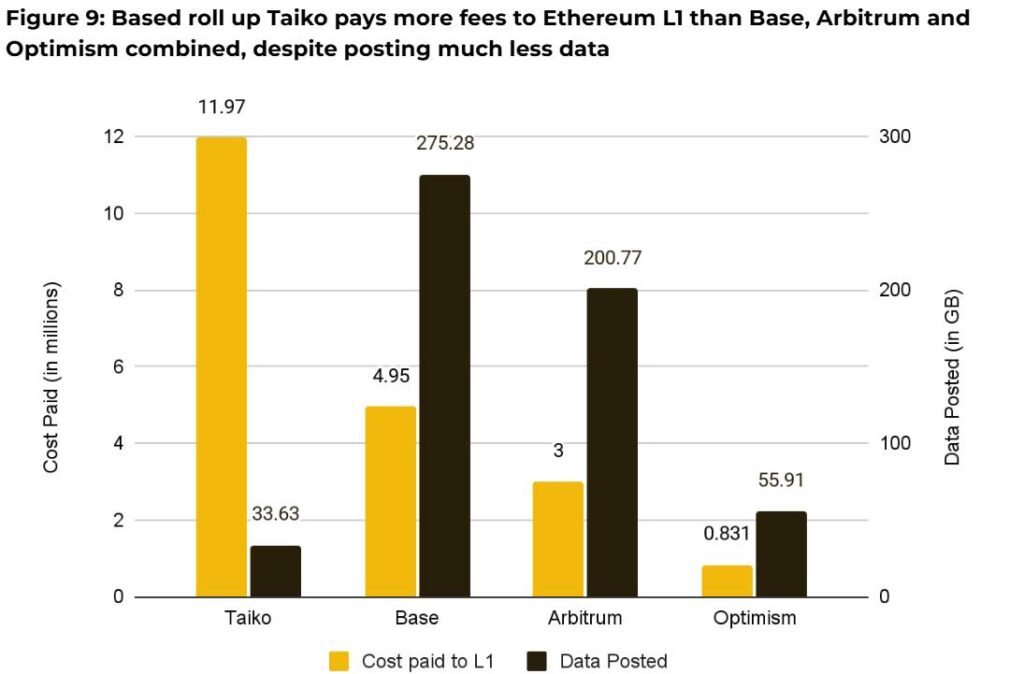
Despite the optimism surrounding these upgrades, the effectiveness of Ethereum’s proposed changes remains uncertain in the short term. As Binance Research notes, aligning incentives between Ethereum and L2s will be crucial. Innovations like rollups, which can generate more fees for the Ethereum network than traditional L2s, could play a key role in restoring value. The need for robust demand for blockspace is underscored, particularly as alternative chains continue gaining traction.
The cryptocurrency community will be closely monitoring how Ethereum navigates this challenging landscape, striving for sustainable growth while balancing the advantages of its L2 developments against the potential risks they pose to Ether’s intrinsic value.
Ethereum’s Layer-2 Scalability and Its Implications for Ether
Ethereum’s transition towards layer-2 (L2) solutions for scalability may influence the cryptocurrency market in significant ways. Here are the key points to consider:
- Potential Cannibalism of Ether’s Value:
- Layer-2 networks might detract from the value and fees accruing to Ethereum’s main layer.
- This could weaken Ether’s overall market value, impacting current and future investors.
- Competitive Threats from Other Blockchains:
- Ethereum’s dominance in decentralized exchanges is challenged by emerging platforms like Solana and BNB Smart Chain.
- These alternatives may fragment liquidity and developer resources, further threatening Ethereum’s market position.
- Transaction Challenges:
- Slow and costly transactions on the Ethereum mainnet are leading to user dissatisfaction and migration to other platforms.
- These challenges are expected to persist despite planned upgrades focusing on scalability and security.
- Upcoming Network Upgrades:
- The Pectra upgrade aims to enhance staking and L2 scalability but won’t immediately solve value accrual issues.
- Fusaka, anticipated in late 2025, will further focus on making Ethereum a more efficient data availability layer.
- Need for Incentive Alignment:
- For Ether to maintain and grow its value, aligning the incentives between Ethereum and L2 networks is crucial.
- Mechanisms like fee sharing and MEV capture could enhance value retention back to ETH as the ecosystem evolves.
“Value accrual through this model depends on external factors: L2s must continue to choose Ethereum for data availability, and blockspace demand must grow.”
Understanding these points can help investors navigate the complexities of the evolving cryptocurrency landscape, particularly in how Ethereum’s strategies may affect their investments in Ether.
Ethereum’s Layer-2 Scalability: A Double-Edged Sword?
The latest report from Binance Research raises concerns about Ethereum’s ambitious move towards layer-2 (L2) blockchain scalability, stating it may inadvertently undermine the core value of Ether. This insight resonates amidst growing competition from platforms like Solana and BNB Smart Chain, which have been eroding Ethereum’s dominance in decentralized exchange (DEX) volumes. While Ethereum’s L2 solutions aim to alleviate issues such as high transaction costs and scalability challenges, they could also create a detrimental scenario where the base Ethereum layer may cannibalize itself.
Competitive Advantages: On one hand, Ethereum’s transition to L2 solutions serves as a vital step toward increasing transaction speed and reducing costs—benefits that stand to enhance user experience and potentially attract new decentralized finance (DeFi) projects. Upgrades like Pectra promise to boost Ether staking and lay the groundwork for a more robust ecosystem by expanding data handling capacity. The forthcoming Fusaka upgrade may further enhance the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), making it attractive to developers seeking efficiency in smart contract execution.
Disadvantages: However, these upgrades may not immediately fortify Ether’s value, as immediate economic incentives for the mainnet remain in flux. The report points out that Ethereum’s economic model may be under pressure as L2s draw engagement away from the mainnet. In a competitive landscape filled with alternatives like Solana, Ethereum’s historical reliability on DEX fees could face considerable threats. This situation leaves Ether in a precarious position, highlighted by its recent price drop to $1,410, the lowest since March 2023.
Beneficiaries and Challenges: The potential beneficiaries of this shifting dynamic are L2 projects that effectively capture developer interest and user engagement. As Ethereum explores pathways toward value accrual through rollups, these solutions could be pivotal. Conversely, developers who favor L2 solutions may find themselves caught in a dilemma; while they could benefit from immediate scalability advantages, they might contribute to a weakened position for Ether as an asset in the long term. Such fragmentation could ultimately lead to liquidity challenges and reduced growth opportunities for Ethereum, given its reliance on mainnet traction for capital infusion.
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, stakeholders will need to closely monitor Ethereum’s balancing act of leveraging L2 advantages without sacrificing core economic viability. Success will hinge on aligning incentive structures across layers, ensuring that both L1 and L2 contribute to a sustainable future for Ether.